Protocol Buffer
Protocol buffer(혹은 protobuf)란, 구글에서 개발한 구조화된 데이터를 직렬화하기 위한 언어 및 플랫폼과 무관한 매커니즘이다.
JSON, XML과 같은 IDL과 유사하지만, 다음의 장점을 가졌다.
- 더 작고(적은 byte로 overhead를 줄일 수 있기 때문) 간단하다.
- 빠르다(Protocol buffer는 binary message 형식이기 때문에, 직렬화/역직렬화 과정이 더 빠름).
- JSON과 같은 데이터 형식에 비해 강력한 스키마 정의를 따르기 때문에 특정 attribute를 수정할 경우, 모든 검증 로직을 수정할 필요가 없다.
Protocol Buffer의 구성
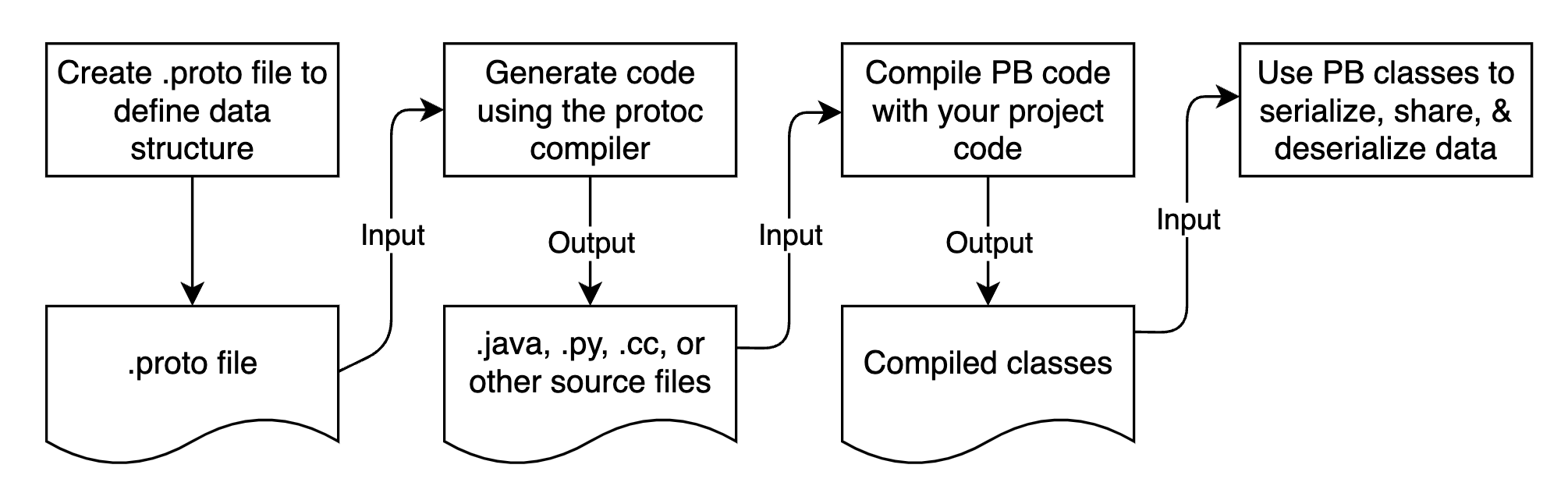
Protocol buffer는 다음의 집합으로 구성된다.
.proto파일에 생성된 정의 언어- 데이터와 상호작용하기 위해 proto compiler(
protoc)가 생성하는 코드 - 언어별 런타임 라이브러리
- 네트워크로 전송되거나 파일에 쓰일 데이터의 직렬화 형식
언제 사용하면 좋을까?
Protocol Buffers Documentation에서는 다음과 같은 장점이 있다고 소개한다.
- 압축된 데이터 저장소
- 빠른 파싱
- 다양한 프로그래밍 언어에서 사용 가능
- 자동 생성되는 클래스를 통한 최적화된 기능
따라서 다음과 같은 경우에 적합하다고 할 수 있다.
- 데이터 타입이 있는 구조화된 데이터를 언어 또는 플랫폼과 무관하게 직렬화하는 경우
- 네트워크 트래픽을 일시적으로 저장하는 경우
- 데이터를 장기간 저장하는 경우
반대로, 언제 사용하지 않아야 할까?
Protocol Buffers Documentation에서는 다음과 같이 적절치 않은 경우를 소개한다.
- 데이터의 크기가 몇 MB를 초과하는 경우
- 동일한 데이터도 직렬화 한 결과가 매우 다양하게 나타나므로, 이를 비교하는 경우, 메시지를 모두 파싱한 뒤 비교할 수 있음
- Protocol buffer 메시지는 self-descriptive하지 않기 때문에,
.proto파일이 있어야 메시지를 해석할 수 있음
Protocol Buffer 동작 예시
예를 들어, 다음과 같은 Person.proto 파일이 있다고 가정하자.
syntax = "proto3";
package example;
message Person {
optional string name = 1;
optional int32 id = 2;
optional string email = 3;
}
Compile
$ protoc --python_out=. ./Person.proto
우선 주어진 proto 파일을 protoc로 컴파일 한 뒤, 위의 명령어로 python 코드를 생성한다. 그러면 Person_pb2.py 파일이 생성된다.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Generated by the protocol buffer compiler. DO NOT EDIT!
# source: Person.proto
"""Generated protocol buffer code."""
from google.protobuf.internal import builder as _builder
from google.protobuf import descriptor as _descriptor
from google.protobuf import descriptor_pool as _descriptor_pool
from google.protobuf import symbol_database as _symbol_database
# @@protoc_insertion_point(imports)
_sym_db = _symbol_database.Default()
DESCRIPTOR = _descriptor_pool.Default().AddSerializedFile(b'\n\x0cPerson.proto\x12\x07\x65xample\"Z\n\x06Person\x12\x11\n\x04name\x18\x01 \x01(\tH\x00\x88\x01\x01\x12\x0f\n\x02id\x18\x02 \x01(\x05H\x01\x88\x01\x01\x12\x12\n\x05\x65mail\x18\x03 \x01(\tH\x02\x88\x01\x01\x42\x07\n\x05_nameB\x05\n\x03_idB\x08\n\x06_emailb\x06proto3')
_builder.BuildMessageAndEnumDescriptors(DESCRIPTOR, globals())
_builder.BuildTopDescriptorsAndMessages(DESCRIPTOR, 'Person_pb2', globals())
if _descriptor._USE_C_DESCRIPTORS == False:
DESCRIPTOR._options = None
_PERSON._serialized_start=25
_PERSON._serialized_end=115
# @@protoc_insertion_point(module_scope)
이렇게 protoc 컴파일러에 의해 Python 코드로 Builder가 생성되었다.
생성된 Builder로 새로운 인스턴스 생성
그런 다음, 새로운 Python 파일에서 이를 다음과 같이 사용할 수 있다.
# proto_python.py
import Person_pb2
def create_person():
person = Person_pb2.Person()
person.name = "John Doe"
person.id = 1234
person.email = "john.doe@example.com"
return person
def serialize_person(person):
with open('person.bin', 'wb') as f:
f.write(person.SerializeToString())
def main():
person = create_person()
print("Person: {}".format(person))
serialize_person(person)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
$ python3 proto_python.py
Person: name: "John Doe"
id: 1234
email: "john.doe@example.com"