Von Neumann Architecture
폰 노이만 아키텍처(Von Neumann Architecture, a.k.a. Von Neumann Model, Princeton Architecture)란, First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC에서 소개된 초기 전자 컴퓨터에 대한 이론이다.
Parts(Organs) of Device
폰 노이만은 해당 이론에서 다음과 같이 Device(일반적으로 Computer)에서 특정 기능을 담당하고 있는 몇 가지 Parts를 인간의 신경계와 장기에 비유해 소개했다.
참고로, 이렇게 비유하는 것에 다음과 같이 첨언을 남겼다.
Following W.S. McCulloch and W. Pitts we ignore the more complicated aspects of neuron functioning: Thresholds, temporal summation, relative inhibition, changes of the threshold by after-effects of stimulation beyond the synaptic delay, etc. It is, however, convenient to consider occasionally neurons with fixed thresholds 2 and 3, that is, neurons which can be excited only by stimuli on 2 or 3 excitatory synapses.
Associative Neurons
뉴런계와 비슷하게 핵심 연산을 담당하는 부분이다.
The three specific parts CA, CC (together C) and M correspond to the associative neurons in the human nervous system.
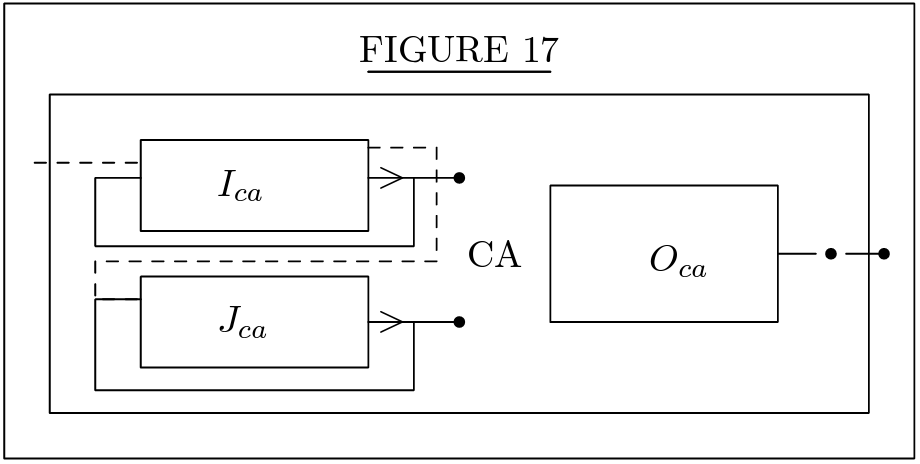
CA: Central Arithmetical
의 기본적인 수치 연산을 수행한다.
CC: Central Control
Device의 명령의 순서를 정의하고 올바르게 수행되는지 검증한다. 명령어는 Storage에 저장 돼 있는데, 이는 CC와 분리 돼 있지만 CC의 실행에 ��필수이다.
M: Memory
많은 양의 연산을 필요로 하며, 특정 연산 결과는 저장 돼야 하고, 테이블 형태로 값 또는 함수를 재사용 하기 위해 상당한 크기의 저장소가 필요하다.
Sensory(afferent) and Motor(efferent) Neurons
감각 또는 운동 뉴런은 입력과 출력을 담당하는 부분이다.
R: Outside Recording Medium of The Device
Device에는 정보를 전달할 수 있는 장기(Organ)가 필요한데, 외부의 자극(또는 입력)을 받고 이를 저장해 외부와 소통할 수 있는 역할을 한다.
I: Input
R를 통해 들어온 정보를 M으로 전달해주는 역할을 담당한다. (절대 직접적으로 C에 전달해주지 않는다.)
O: Output
반대로, C와 M에서 R로 전달하는 역할을 담당한다.
이들을 요약하면 다음과 같이 표현할 수 있다.
M stores, CC administers, and I, O maintain the connections with the outside.
Circuits For The Arithmetical Operations
adder network
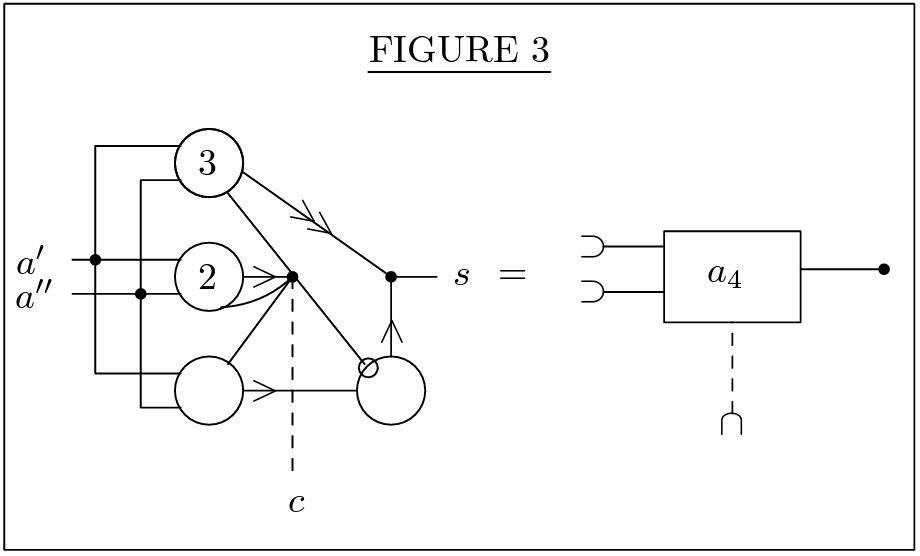
multiplier network
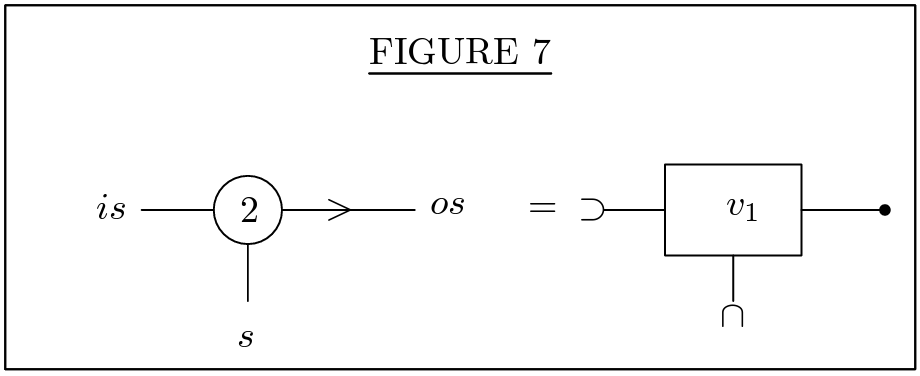
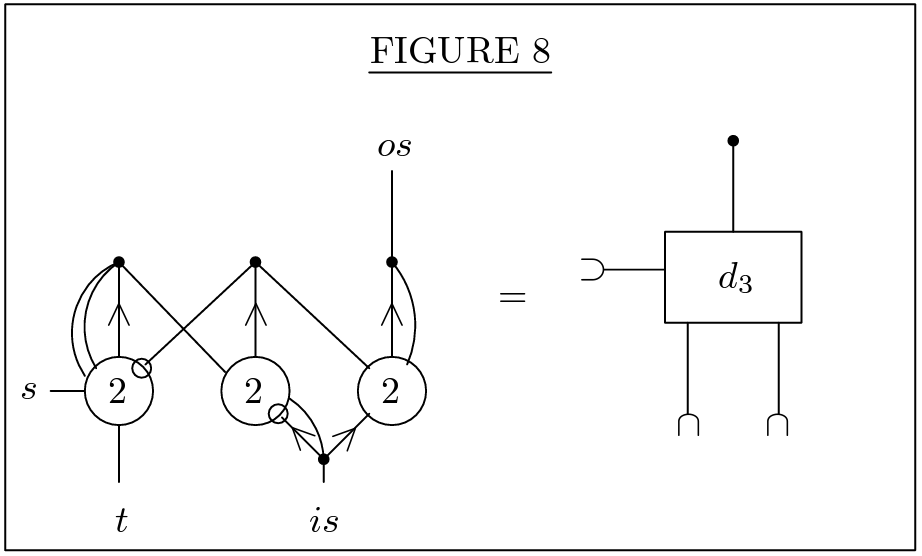
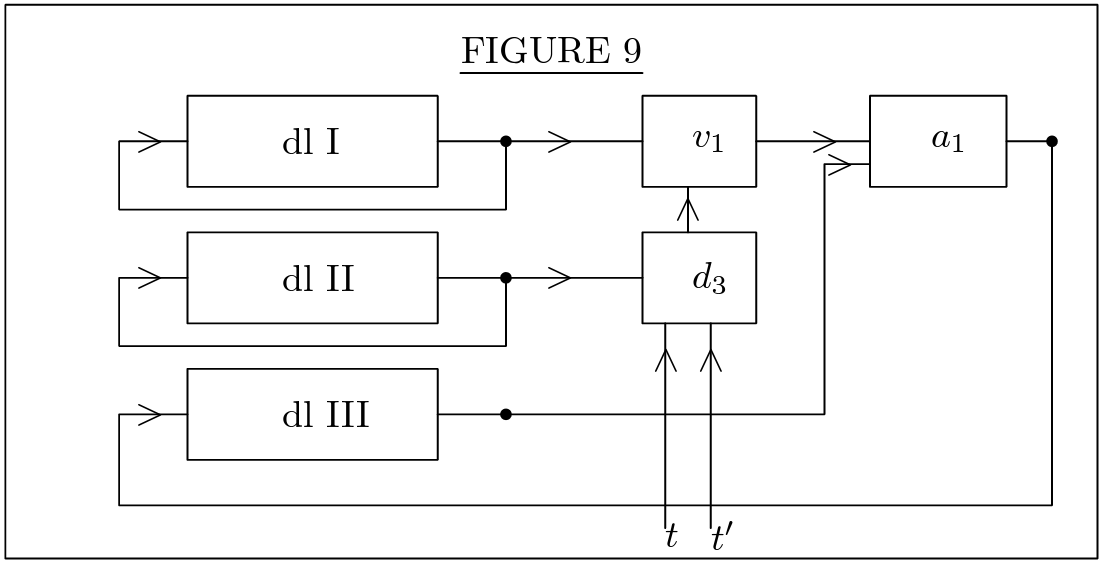
subtracter network
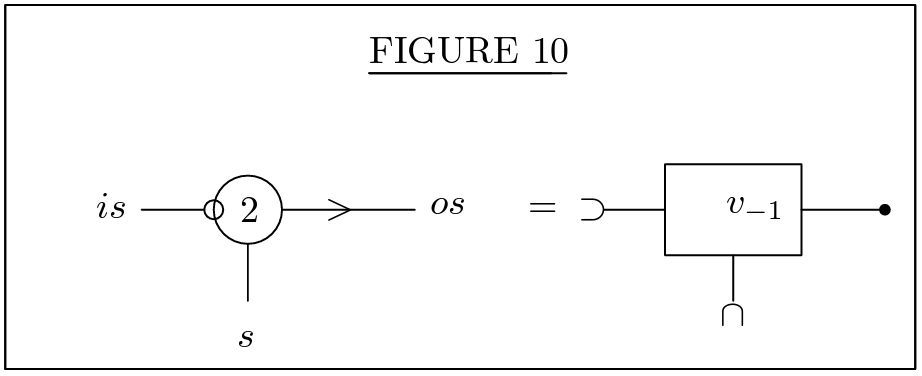
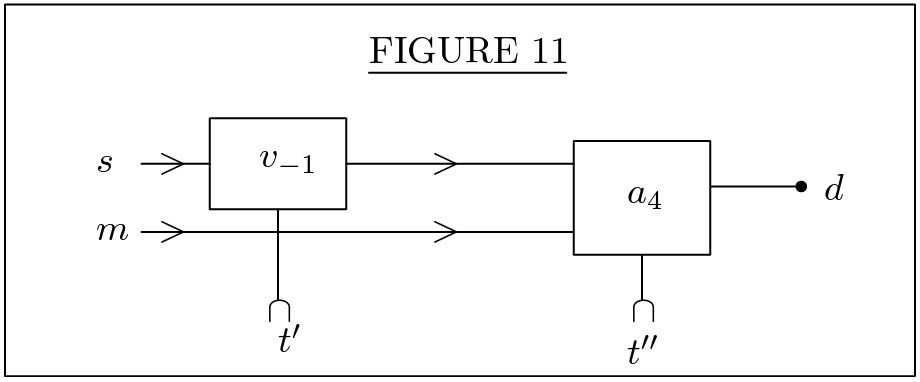
divider network
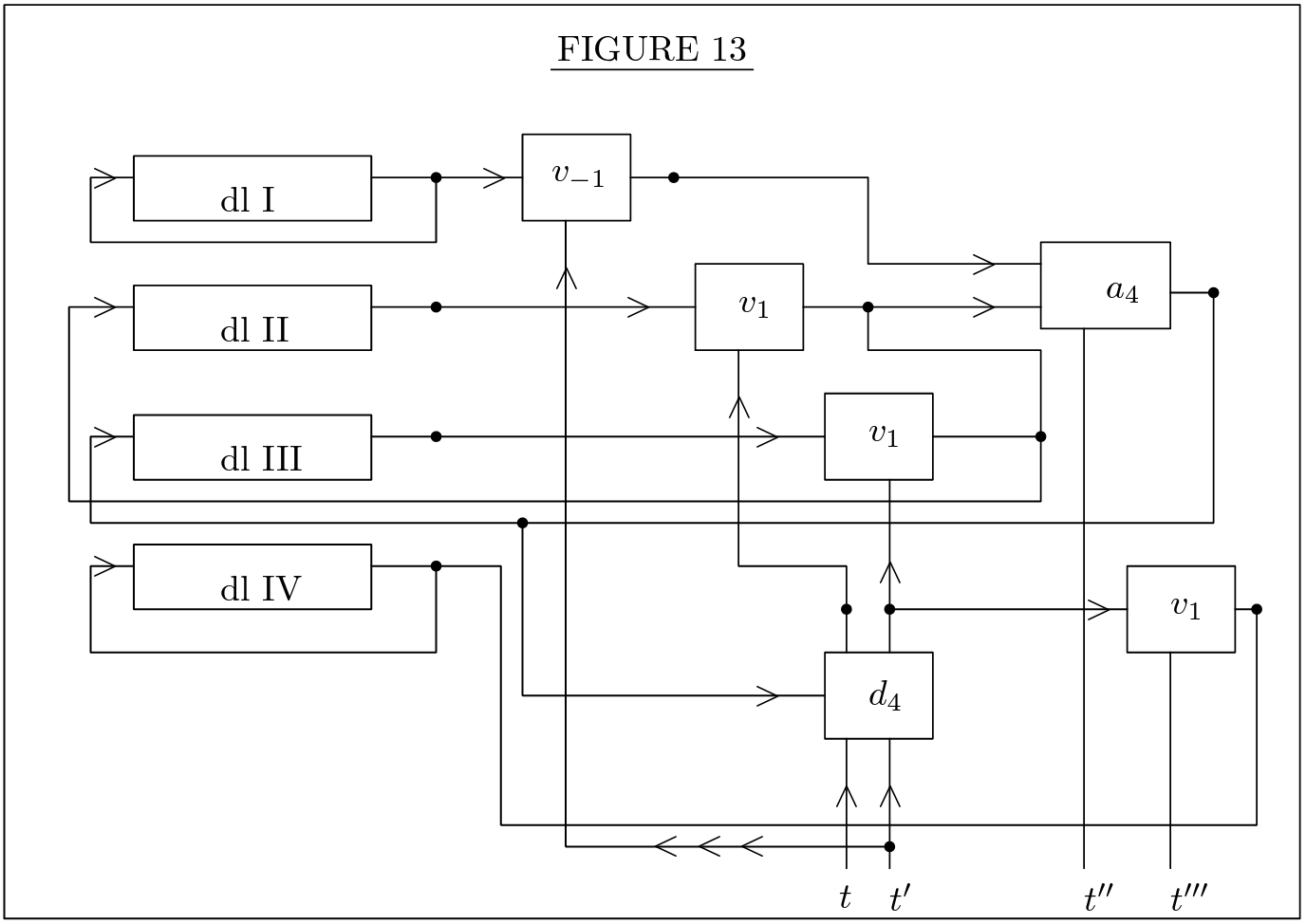
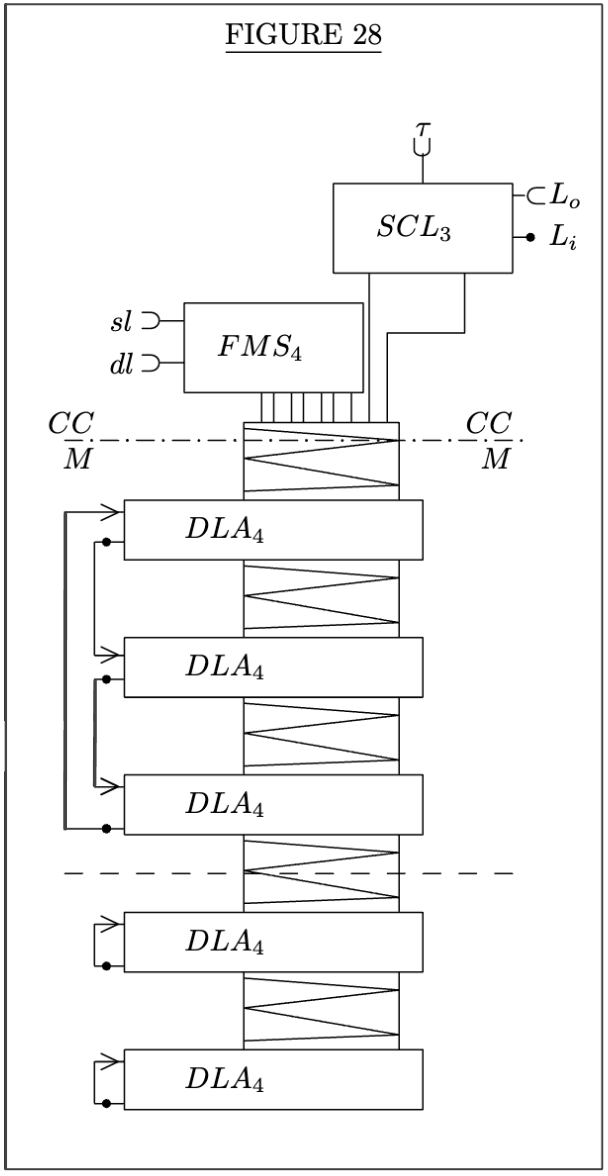
Final Organizations
각 연산()에 대해 폰 노이만 기호와 함께 제시했다. 이를 조합해 다음과 같은 결과물을 얻을 수 있다.
CA with Complete List of Operations
M
CC and M